
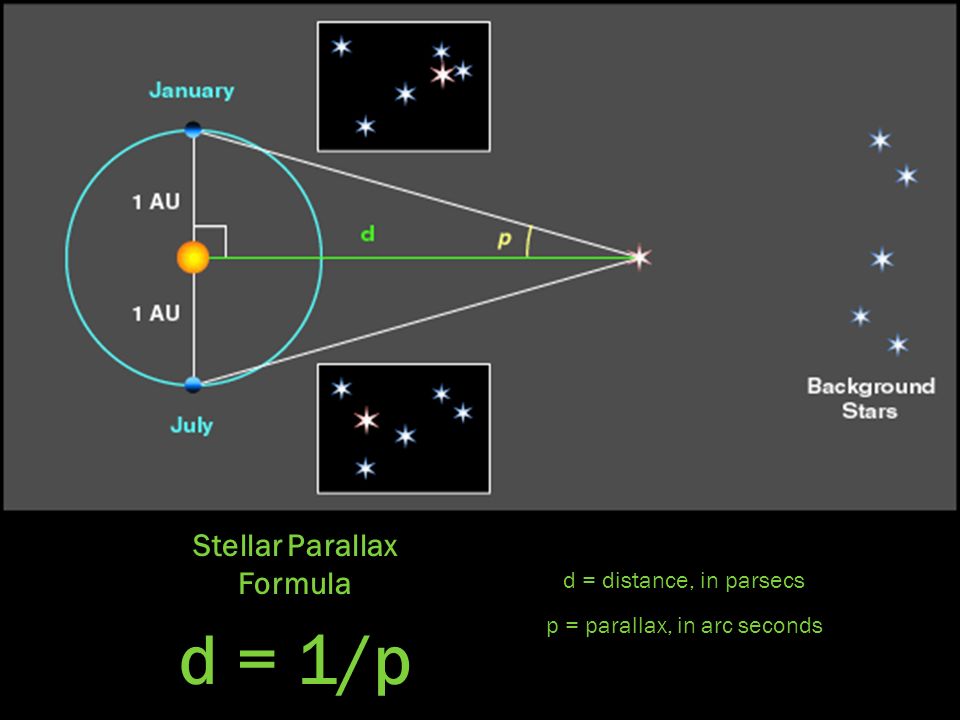
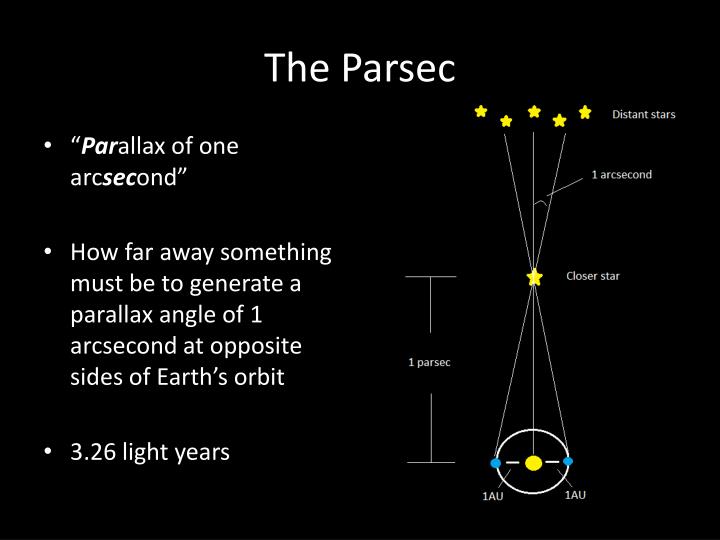
This occurs because each eye sees a slightly different view because they are separated by a few inches. Close one eye, then the other and notice how your finger appears to move in relation to the background. The principal of Parallax can easily be demonstrated by holding your finger up at arm's length. For stars outside our galaxy we can use cepheid variables, supernovae and redshift.įor Stars within our Galaxy Using Parallax to Measure DistanceĪstronomers use an effect called parallax shift to measure distances to nearby stars.
 For stars within our galaxy we can use distance modulus or parallax. There are various methods for measuring distance in space and a different method is used depending on how far away the target is. Comparing Distances in Space DistanceĮarth to the edge of the visible Universe The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax which includes 10,000 galaxies of various ages, sizes, shapes, and colours. We are effectively looking back in time, to a point only a few hundred million years after the big bang. Because we know how far away it is, and that the speed of light is constant, we know that the light from that galaxy has travelled for 13.2 billion years to arrive here. The furthest observed galaxy is EGS8p7 which is more than 13.2 billion light years away. The Andromeda galaxy is the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way, and at a distance of 2.5 million light years, it's quite a bit further than walking down the road to the chemist. Even using light years as a measure of distance we still deal with very large numbers. We simply move the decimal place to the left until we get to the smallest significant figure and count the number of times we moved the decimal place. One light-year is equal to 9,500,000,000,000 kilometers, or 63,241 AU.įor large numbers like this, we often use scientific notion. In one year, light travels about 10 trillion km. Light travels at around 300,000 kilometres per second, so these numbers can get very big, very fast. Since the speed of light is constant, the distance is also constant. A light year is defined as the distance light travels in a year. If you want to convert AU to KM or Miles, simply multiply the Earths orbital radius by the AU value.įor distances outside of the solar system, the light year distance is often used. These values are much easier to work with. Earth being 1AU, Venus at 0.72AU, Jupiter at 5.2AU. You can see why we don't express this as kilometres! For objects in the solar system, their orbits are typically given in terms of the Astronomical Unit (AU).
For stars within our galaxy we can use distance modulus or parallax. There are various methods for measuring distance in space and a different method is used depending on how far away the target is. Comparing Distances in Space DistanceĮarth to the edge of the visible Universe The Hubble Ultra Deep Field is an image of a small region of space in the constellation Fornax which includes 10,000 galaxies of various ages, sizes, shapes, and colours. We are effectively looking back in time, to a point only a few hundred million years after the big bang. Because we know how far away it is, and that the speed of light is constant, we know that the light from that galaxy has travelled for 13.2 billion years to arrive here. The furthest observed galaxy is EGS8p7 which is more than 13.2 billion light years away. The Andromeda galaxy is the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way, and at a distance of 2.5 million light years, it's quite a bit further than walking down the road to the chemist. Even using light years as a measure of distance we still deal with very large numbers. We simply move the decimal place to the left until we get to the smallest significant figure and count the number of times we moved the decimal place. One light-year is equal to 9,500,000,000,000 kilometers, or 63,241 AU.įor large numbers like this, we often use scientific notion. In one year, light travels about 10 trillion km. Light travels at around 300,000 kilometres per second, so these numbers can get very big, very fast. Since the speed of light is constant, the distance is also constant. A light year is defined as the distance light travels in a year. If you want to convert AU to KM or Miles, simply multiply the Earths orbital radius by the AU value.įor distances outside of the solar system, the light year distance is often used. These values are much easier to work with. Earth being 1AU, Venus at 0.72AU, Jupiter at 5.2AU. You can see why we don't express this as kilometres! For objects in the solar system, their orbits are typically given in terms of the Astronomical Unit (AU). 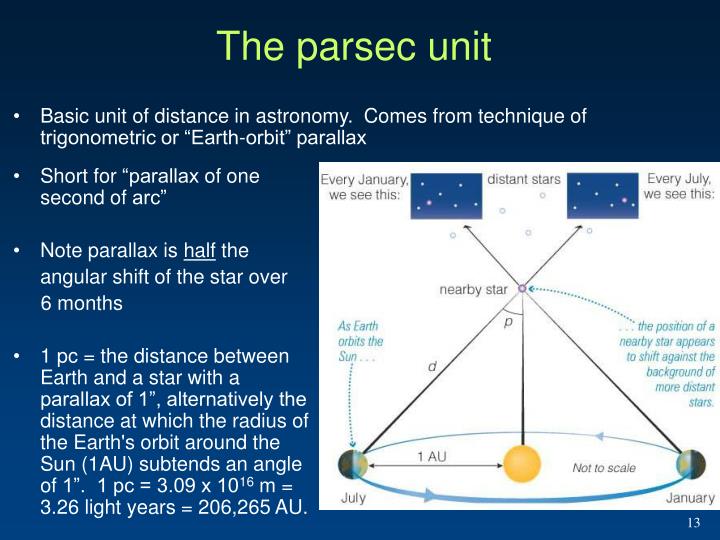
We say average because the Earths orbit is elliptical, varying from a maximum (aphelion) to a minimum (perihelion) and back again once a year.Įlliptical Orbits - Aphelion, Perihelion, Perigee, Apogeeĭue to this variation, the Astronomical Unit is now defined as exactly 149,597,870,700 metres (about 150 million kilometres, or 93 million miles). The Astronomical Unit is the average distance from Earth to the Sun. Douglas Adams, The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy I mean, you may think it's a long way down the road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space. You just won't believe how vastly, hugely, mind-bogglingly big it is. In modern astronomy, we often use the Astronomical Unit or the Lightyear. When we realised just how big space was, we needed some new units. Far too many to describe them in terms of miles or kilometres. When we talk about distance in astronomy, we are usually talking very, very large numbers. Using Cepheid Variables to Calculate Distance.Using Distance Modulus to Calculate Distance.How Are Astronomical Distances Measured?.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
